|
1 | | -688\. Knight Probability in Chessboard |
| 1 | +689\. Maximum Sum of 3 Non-Overlapping Subarrays |
2 | 2 |
|
3 | | -Medium |
| 3 | +Hard |
4 | 4 |
|
5 | | -On an `n x n` chessboard, a knight starts at the cell `(row, column)` and attempts to make exactly `k` moves. The rows and columns are **0-indexed**, so the top-left cell is `(0, 0)`, and the bottom-right cell is `(n - 1, n - 1)`. |
| 5 | +Given an integer array `nums` and an integer `k`, find three non-overlapping subarrays of length `k` with maximum sum and return them. |
6 | 6 |
|
7 | | -A chess knight has eight possible moves it can make, as illustrated below. Each move is two cells in a cardinal direction, then one cell in an orthogonal direction. |
| 7 | +Return the result as a list of indices representing the starting position of each interval (**0-indexed**). If there are multiple answers, return the lexicographically smallest one. |
8 | 8 |
|
9 | | -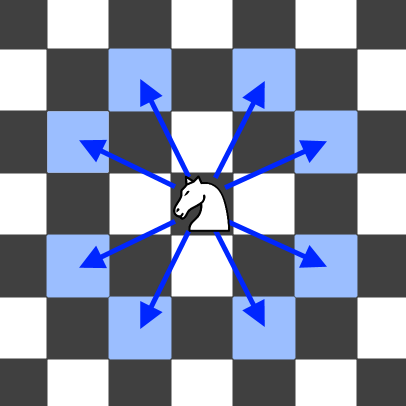 |
10 | | - |
11 | | -Each time the knight is to move, it chooses one of eight possible moves uniformly at random (even if the piece would go off the chessboard) and moves there. |
12 | | - |
13 | | -The knight continues moving until it has made exactly `k` moves or has moved off the chessboard. |
| 9 | +**Example 1:** |
14 | 10 |
|
15 | | -Return _the probability that the knight remains on the board after it has stopped moving_. |
| 11 | +**Input:** nums = [1,2,1,2,6,7,5,1], k = 2 |
16 | 12 |
|
17 | | -**Example 1:** |
| 13 | +**Output:** [0,3,5] |
18 | 14 |
|
19 | | -**Input:** n = 3, k = 2, row = 0, column = 0 |
| 15 | +**Explanation:** |
20 | 16 |
|
21 | | -**Output:** 0.06250 |
| 17 | +Subarrays [1, 2], [2, 6], [7, 5] correspond to the starting indices [0, 3, 5]. |
22 | 18 |
|
23 | | -**Explanation:** There are two moves (to (1,2), (2,1)) that will keep the knight on the board. From each of those positions, there are also two moves that will keep the knight on the board. The total probability the knight stays on the board is 0.0625. |
| 19 | +We could have also taken [2, 1], but an answer of [1, 3, 5] would be lexicographically larger. |
24 | 20 |
|
25 | 21 | **Example 2:** |
26 | 22 |
|
27 | | -**Input:** n = 1, k = 0, row = 0, column = 0 |
| 23 | +**Input:** nums = [1,2,1,2,1,2,1,2,1], k = 2 |
28 | 24 |
|
29 | | -**Output:** 1.00000 |
| 25 | +**Output:** [0,2,4] |
30 | 26 |
|
31 | 27 | **Constraints:** |
32 | 28 |
|
33 | | -* `1 <= n <= 25` |
34 | | -* `0 <= k <= 100` |
35 | | -* `0 <= row, column <= n - 1` |
| 29 | +* <code>1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 10<sup>4</sup></code> |
| 30 | +* <code>1 <= nums[i] < 2<sup>16</sup></code> |
| 31 | +* `1 <= k <= floor(nums.length / 3)` |
0 commit comments