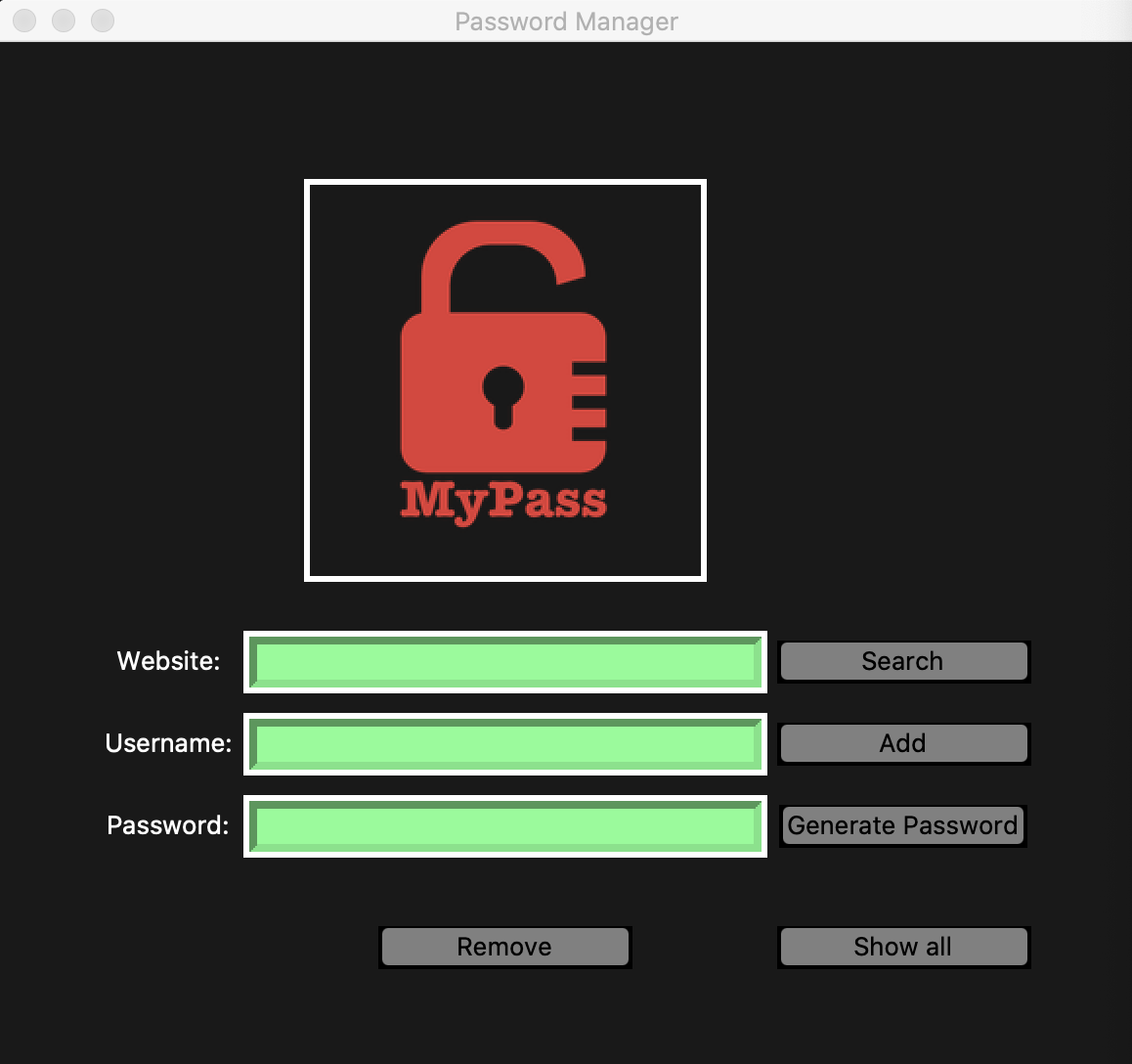
Desktop app to generate strong passwords and locally store your various login info to database in a secure format using symmetric encryption.
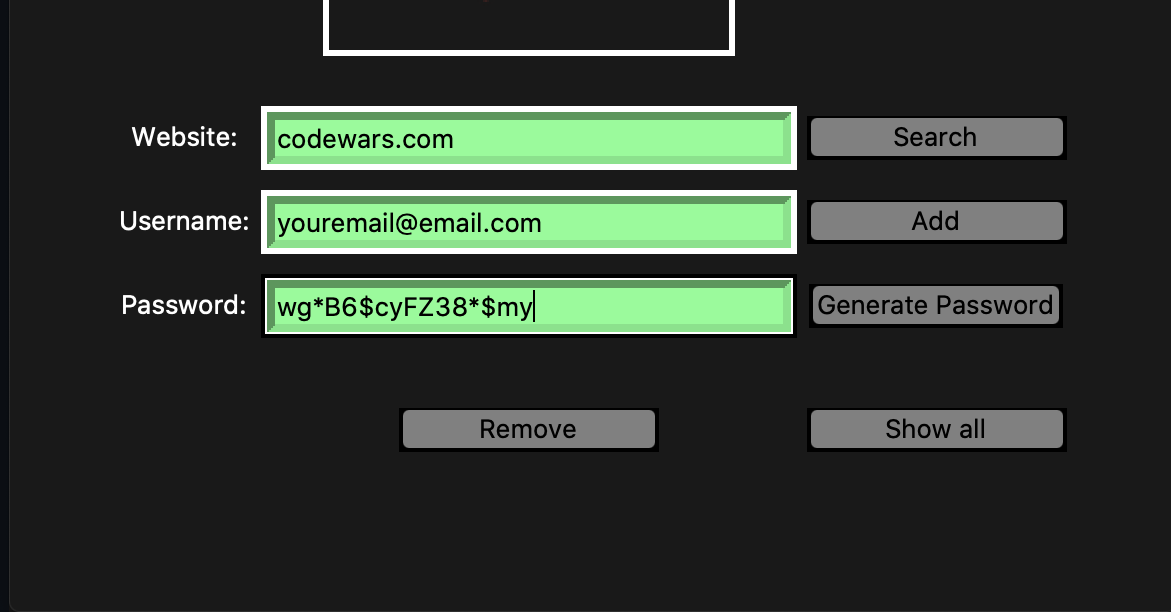
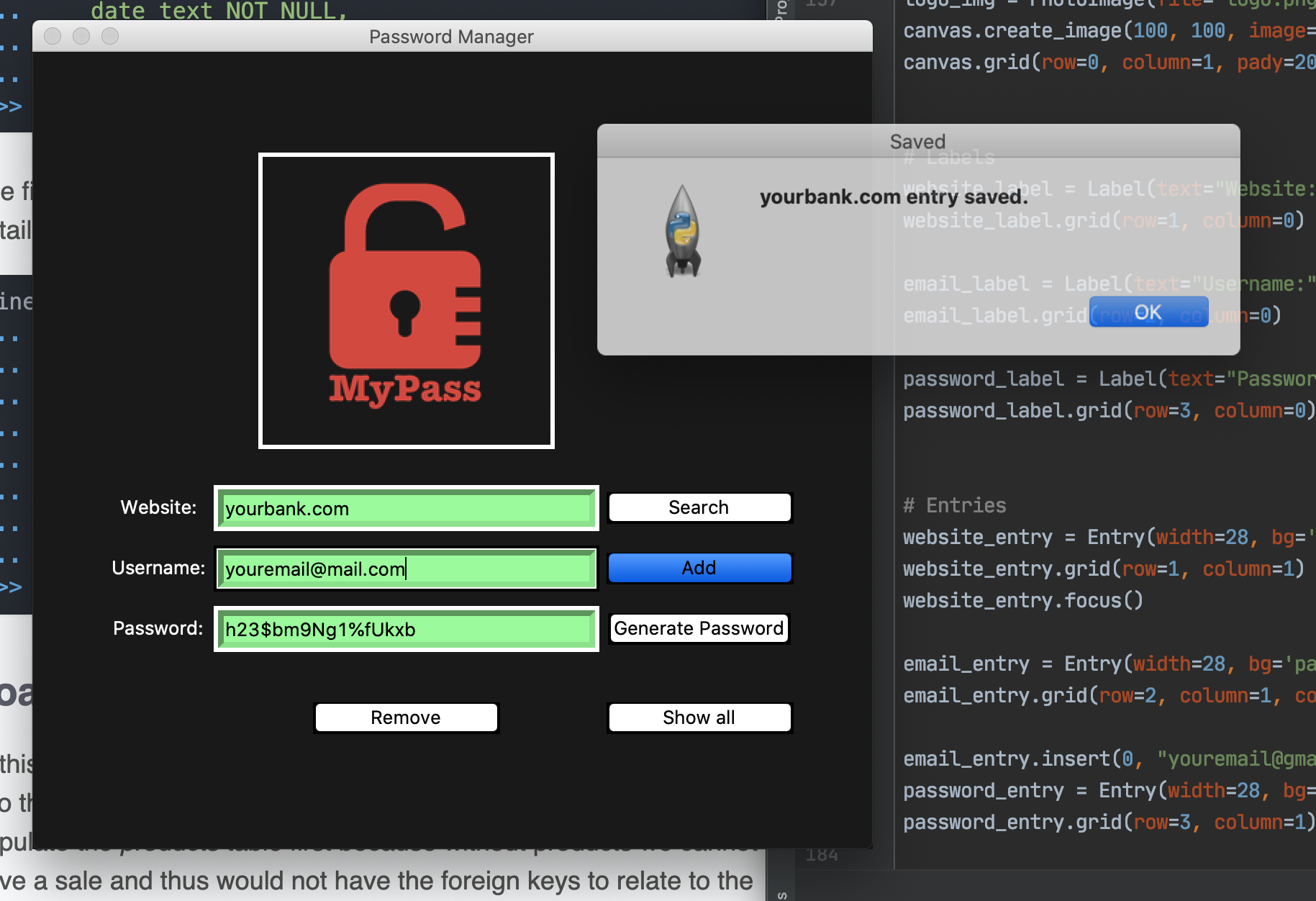
A secure vault for your collective login credentials with features including, a randomized password generator, a local database, that you will only have access to, where you can save, search, and delete the contents. Requiring the dual authentication of your master password and the generated "key". Your data will be safely kept using an encryption method which makes sure that the message encrypted cannot be manipulated/read without the key. It uses URL safe encoding for the keys. Fernet also uses 128-bit AES(Advanced Encryption Standard), in CBC(Cipher Block Chaining) mode and PKCS7 padding, with HMAC using SHA256 for authentication.
Having your data stored using encryption adds a layer of security. This means that if someone was to directly access the database the information within it would be in an unreadable form. User names and passwords should never be stored in plain text.
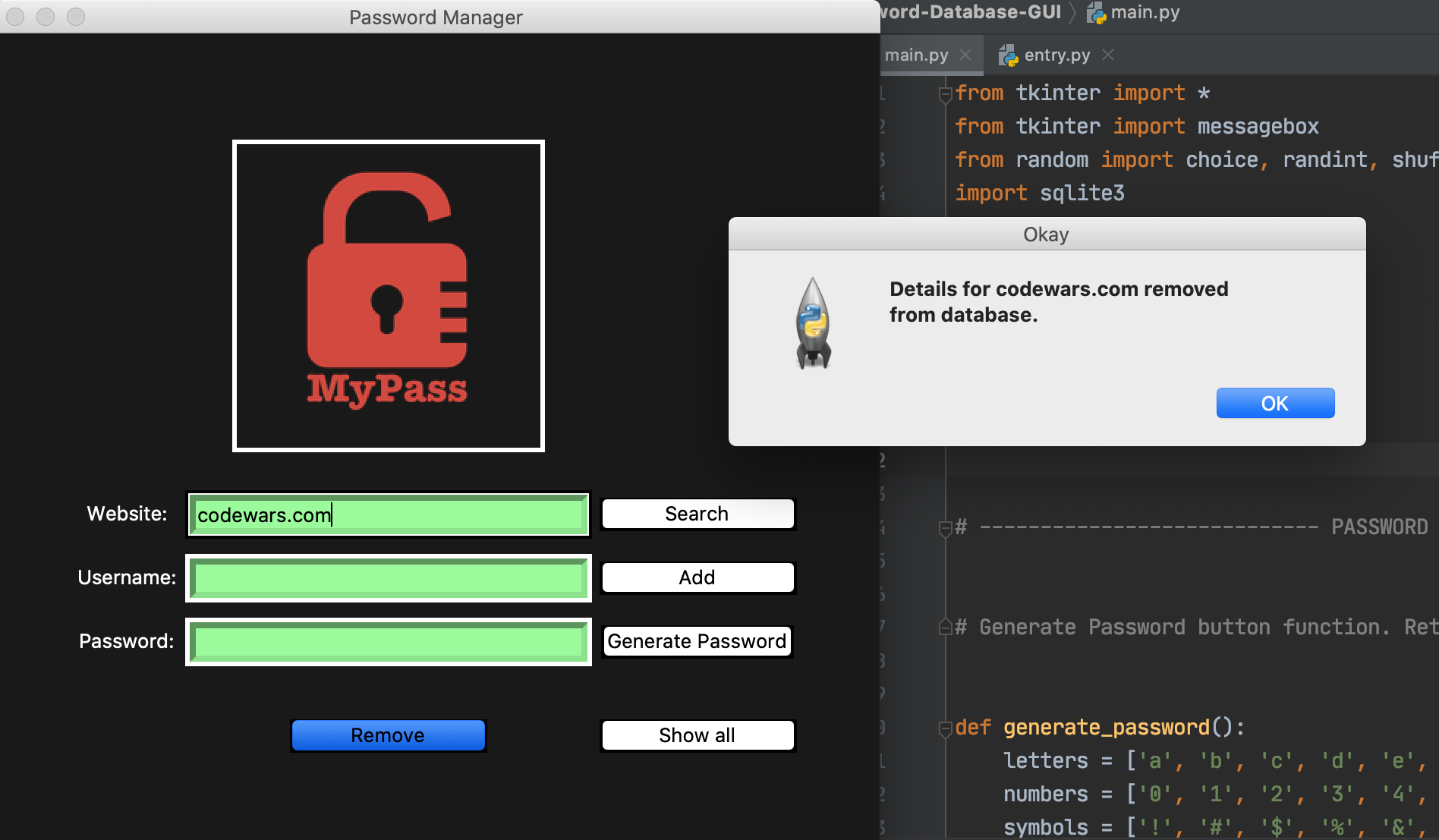
Only the 'Key' will be able to convert your data back (decrypt) to it's original readable text format. This is what is referred to as symmetric encryption. The same key is used for both by both the sender and the receiver. Only the holder of this Key has the ability to encrypt and decrypt the contents stored in the data base. Encrypts them after they are entered, then decrypts them before we request information from the database.
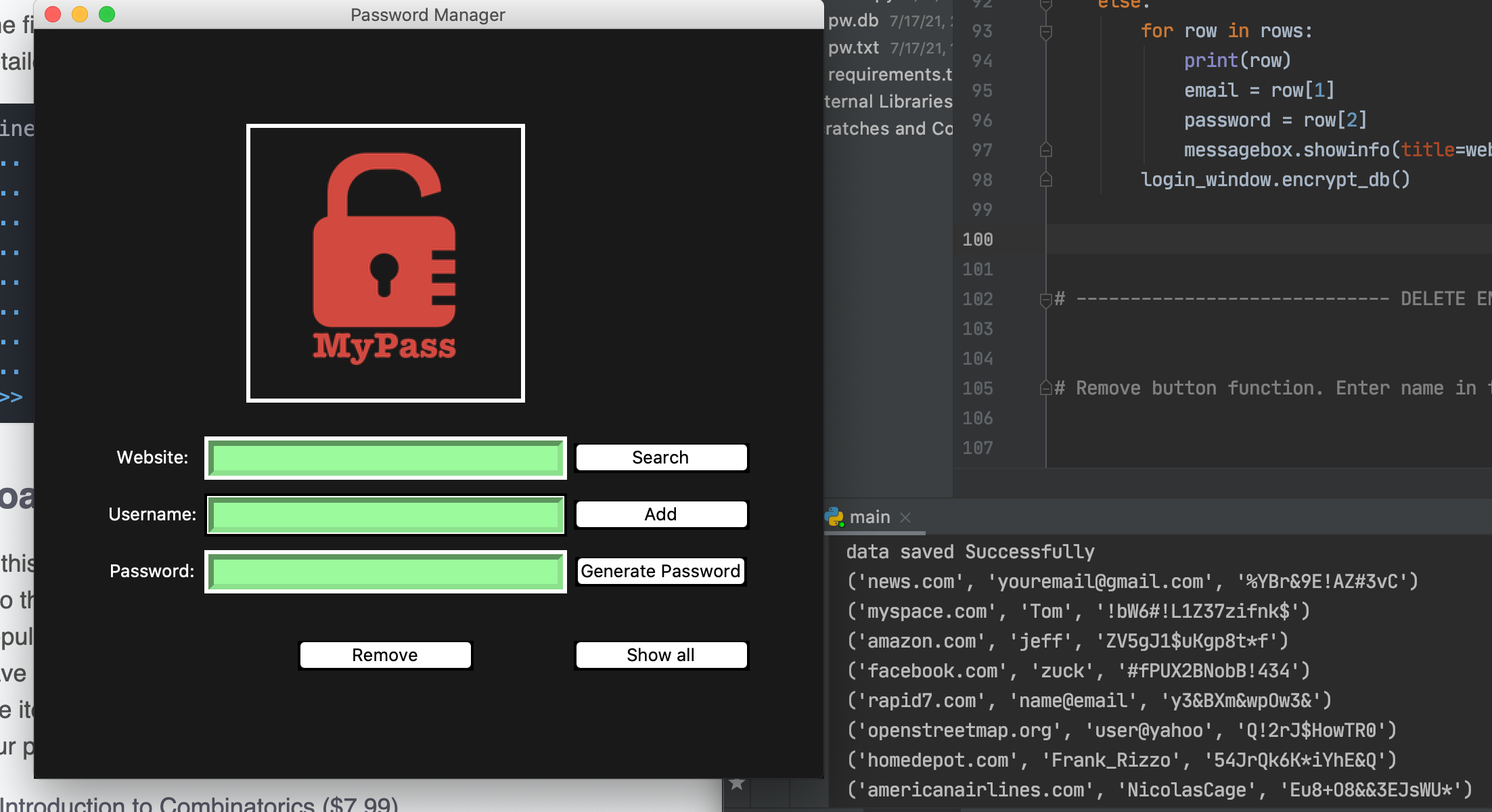
Built with Python3 and Tkinter library for the user interface. Sqlite3 is the database that stores your login credentials organized as seperate entries for each website or app that requires log info. We will use the Python library, Cryptography. In the cryptography library, there is a cryptography algorithm called fernet. We will use the fernet module to encrypt the file.
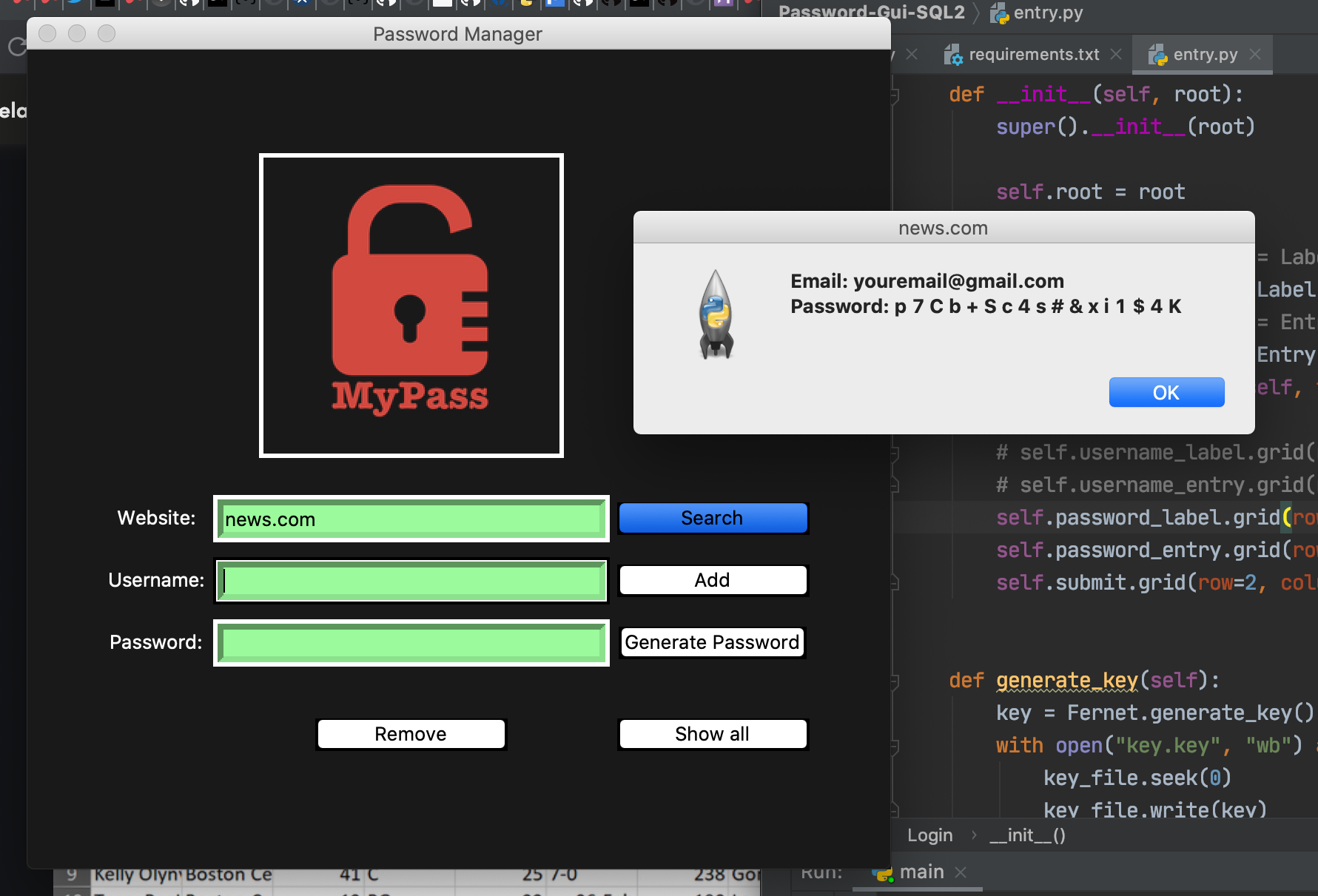
Displays the credentials from your search result in a messagebox window, also prints them to the terminal.
For transparency's sake, keep in mind this app is just a personal project for personal use, meant for a single user on their local machine. I would not recommend giving it a whirl in any corporate or shared settings with highly sensitive data or client/employee information.
That being said, let's have a deeper look into how the key - encryption relationship works, and why you must keep your key private - here is an example:
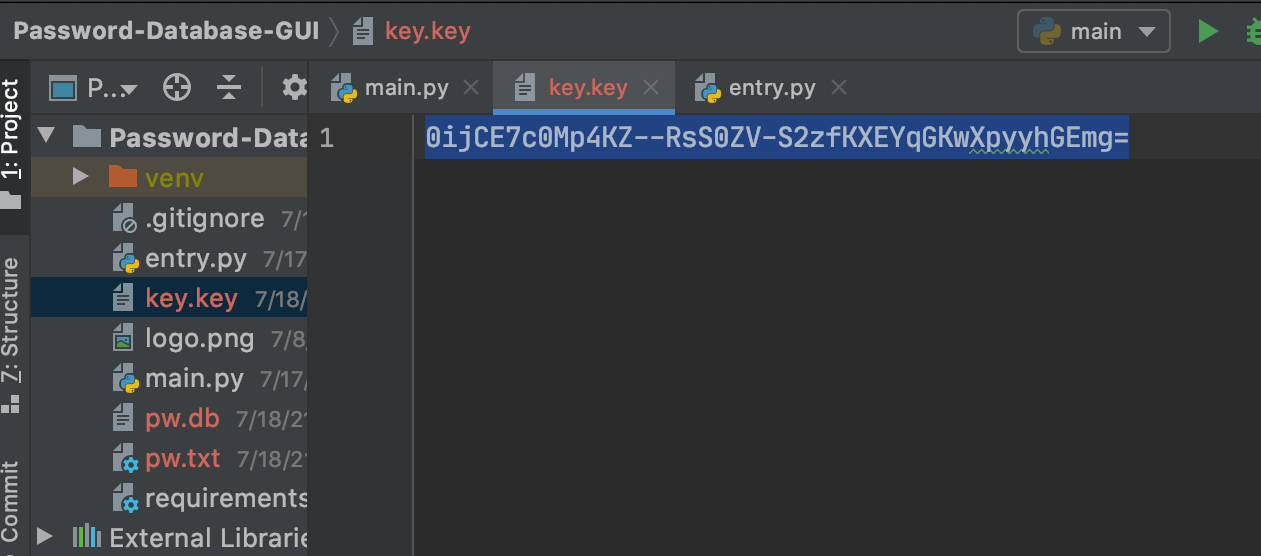
The master password is stored encrypted, so if pw.txt was accessed your password would be unreadable and if you were to directly view the contents of your encrypted database file it would look something like this:
But, if they were to get your Key, they can decrypt your password and now have the authentication required to start the decryption process and get all of your data in plain text format.
- See code below:
# string from key.key
key_str = 'bWyo52t1dSnwi-KpvLM2OhUsn-i1jeV-MLuPj9Ud2cw='
key = str.encode(key_str)
# actual encrypted version of master password(123) from pw.txt
password_str = 'gAAAAABg77PHASqKZlKkQOuNersMJEBl3JVpBhJebbI0emQK_lbU9HOfQnPi2vIAcVmczyapwsJk_HrlDd514_2Xz6qMmHKiPQ=='
password = str.encode(password_str)
f = Fernet(key)
plain_text = f.decrypt(password)
print(plain_text)
# output:
# b'123'